
Owning property isn’t just an investment; it’s a responsibility. Whether you’re renting out a cozy single-family home or managing multiple commercial units, your assets are vulnerable to risks like natural disasters, accidents, or tenant damages. This is where landlord insurance steps in. A reliable safety net that lets you focus on maximizing your investment returns with peace of mind.
But what exactly does landlord insurance cover? How much does it cost? And how do you choose the right policy? If you’re asking these questions as a property owner, you’re in the right place. In this guide, we’ll break down landlord insurance, covering everything from the types of policies available to real-life examples of how it has protected property owners.
Table of Contents
- What is Landlord Insurance?
- What Does Landlord Insurance Cover?
- How Much Does Landlord Insurance Cost?
- The Cost of the Different Types of Landlord Insurance Coverage
- Tips for Lowering Landlord Insurance Rates
- How to Choose the Right Landlord Insurance Policy
- Conclusion: Protect Your Property and Have Peace of Mind
What is Landlord Insurance?
Landlord insurance is a type of property insurance designed to protect property owners from financial risks associated with renting out a home or apartment.
Unlike standard homeowner’s insurance, which only covers owner-occupied homes, landlord insurance protects against losses related to renting out a property, such as damages from fire, theft, or severe weather. Additionally, it can be extended to cover issues such as unpaid rent and intentional damage caused by tenants, providing landlords with greater financial security.
What Does Landlord Insurance Cover?

A comprehensive landlord insurance policy protects property owners from financial risks associated with renting out their homes. While coverage varies by provider, most policies include these three types of loss:
Property Damage Coverage
Landlord property coverage is primarily about protecting the physical structures that you rent out. This coverage may extend to additional structures such as a garage, fence, or shed.
Some policies also cover the landlord’s personal property used for rental purposes, such as kitchen appliances, washers, dryers, and on-site maintenance tools.
For example, if a storm causes a tree to crash through your rental’s roof, landlord insurance helps cover repair costs. Property damage insurance typically includes coverage for fire, windstorms, and vandalism. However, certain natural disasters, such as floods or earthquakes, often require separate coverage.
Liability Coverage
What if a tenant or visitor slips and gets injured on your rental property and decides to take legal action? And given that personal injury claims are a $38 billion business in the U.S., even diligent landlords can face legal action. That’s where landlord liability coverage steps in.
Liability insurance protects you from lawsuits arising from accidents where you’re found responsible. When you are faced with unpredictable legal challenges, medical payments, and other damages that might come with property management, having liability coverage is often considered essential.
Loss of income Coverage
If a covered event like a fire or storm renders your rental property uninhabitable, loss of rental income coverage ensures you don’t lose your cash flow. This protection compensates you for lost rent while repairs are being made.
NOTE: Some policies only cover loss of income due to physical damage (e.g., fire), while others include broader scenarios like tenant default.
Insurance providers may require proof of your rental income to process a claim, so keeping accurate financial records is critical. Using rental property management tools like Stessa can help track income and expenses, making it easier to provide documentation when filing a claim and ensuring smooth financial operations.
Additional Coverage
Beyond the above standard insurance coverage, landlords can enhance their policies with optional riders that provide extra protection against specific risks. These add-ons may not be essential for everyone, but they can come in handy and save you significant money in the long run.
- Tenant damage coverage: Not all tenants take care of the spaces they occupy. From unintended structural damages to accidental fires, the spectrum of potential mishaps and unexpected repairs can be vast. This coverage ensures you’re not left footing the entire bill for tenant-caused damage.
- Umbrella insurance coverage: An umbrella insurance policy offers additional liability protection. It even includes scenarios not covered by your primary policy, making it an affordable option to avoid possible catastrophic financial blows. This is especially valuable for landlords with multiple properties.
- Earthquake insurance coverage: In earthquake-prone states like California, landlords should consider adding this coverage. Standard policies don’t typically cover earthquake damage while others offer limited coverage. This may leave you vulnerable to costly repairs.
- Flood insurance coverage: With 90% of U.S. natural disasters involving flooding, this coverage is crucial in high-risk areas. Even minor flooding can cause tens of thousands of dollars in damage.
- Terrorism insurance coverage: Following the 9/11 attack that resulted in more than $27M in insured property losses, insurers also offer terrorism coverage, which may be worth considering, especially for properties in major cities as they may be vulnerable to terrorist attacks due to factors such as symbolic targets, critical infrastructure, and high population density.
- Building code coverage: If significant repairs are needed, cities may require you to update older properties to meet modern building codes. This landlord insurance coverage helps cover those upgrade costs.
How Much Does Landlord Insurance Cost?

Landlord insurance typically costs about 25% more than a standard home insurance policy. Based on an analysis by Insurance.com, if the average homeowner’s insurance premium is $2,601 per year, landlords can expect to pay around $3,251 annually.
However, the actual cost of landlord insurance varies significantly depending on location. Some states have notably higher rates due to increased risks such as natural disasters and higher property values.
For example:
- Oklahoma: With an average home insurance premium of $5,858 per year, landlord insurance may reach approximately $7,323 annually.
- Florida: Home insurance averages $4,419 per year, making landlord insurance costs around $5,524.
- Colorado: Homeowners pay an average of $4,099 annually, so landlord insurance could be roughly $5,124.
On the other hand, some states offer more affordable landlord insurance rates due to lower risks and property values. For example:
- Hawaii: With home insurance averaging $613 per year, landlord insurance may cost around $766 annually.
- New Hampshire: Home insurance costs about $1,221 per year, so landlord coverage might be around $1,526.
- California: Home insurance averages $1,405 per year, making typical landlord insurance rates approximately $1,756.
While these estimates provide a general idea, landlord insurance premiums depend on factors such as the following:
Property Location
The location of your rental property significantly impacts insurance costs. Properties in high-risk areas prone to natural disasters such as hurricanes, floods, or earthquakes typically have higher premiums due to the increased likelihood of damage.
Similarly, homes in urban areas with higher crime rates may also face elevated insurance costs compared to those in rural locations, where risks like theft and vandalism tend to be lower.
Property Type and Age
The type and age of your rental property play a crucial role in determining insurance costs. Single-family homes, multi-unit buildings, and apartments each present different risk levels, which can impact premiums.
Older properties often come with higher insurance costs due to increased maintenance needs and the potential for system failures, such as outdated plumbing or electrical wiring, which pose greater risks for damage and liability.
Coverage Limits and Deductibles
Coverage limits and deductibles significantly influence rental property insurance costs. Higher coverage limits offer greater financial protection but result in increased premiums.
Conversely, choosing a higher deductible can reduce premium costs, though it requires the property owner to pay more out-of-pocket in the event of a claim. Balancing coverage needs with affordability is key to managing insurance expenses effectively.
Additional Structures and Features
Additional structures and features on a rental property can increase insurance costs due to heightened risks. Amenities like pools, hot tubs, and detached garages may lead to higher premiums as they pose greater liability concerns or necessitate extra coverage for potential damage.
Insurers factor in these risks when determining policy rates, making it essential for property owners to assess the impact of such features on their overall insurance expenses.
Theft and Crime Risk
Rental properties located in high-crime areas or with a history of break-ins typically have higher insurance premiums due to the increased risk of theft and vandalism. Insurers assess crime rates in the property’s vicinity when determining coverage costs, as properties in such areas are more likely to experience losses.
Implementing security measures like alarm systems, surveillance cameras, and reinforced locks can help mitigate risks and potentially lower insurance expenses.
The Cost of the Different Types of Landlord Insurance Coverage
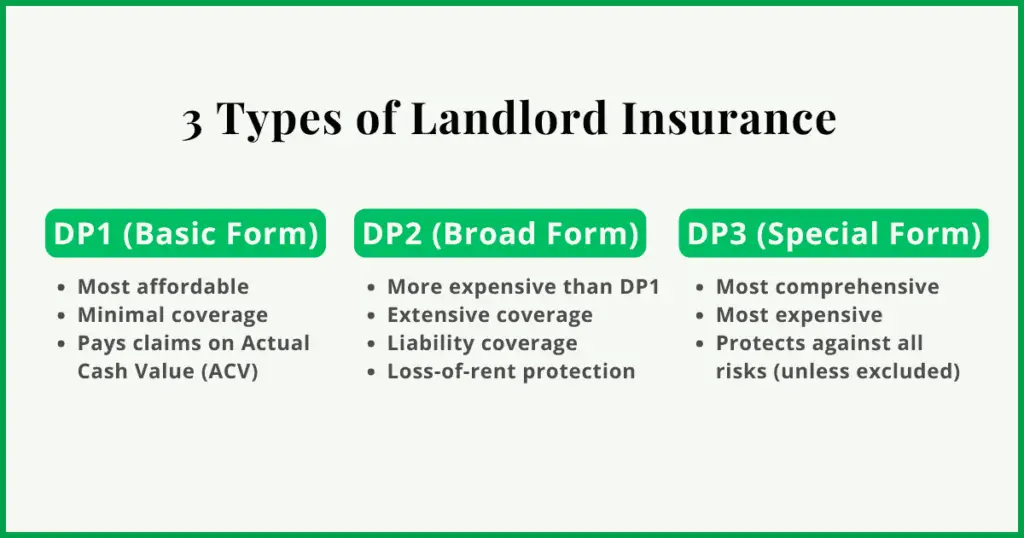
The cost of landlord insurance also varies depending on the type of policy you choose. There are three main types: DP1, DP2, and DP3, each offering different levels of protection at different price points.
DP1 Policy (Basic Form)
A DP1 policy is the most affordable but offers minimal coverage. It only protects against named perils such as fire, lightning, and internal explosions. By default, it pays claims based on actual cash value (ACV). However, some insurers allow upgrades to replacement cost coverage for better protection.
This policy is ideal for landlords with older properties or those looking for basic protection. However, it typically does not include landlord liability insurance or loss-of-rent coverage, though some insurers offer these as optional add-ons.
DP2 Policy (Broad Form)
A DP2 policy is a mid-tier option that provides more extensive coverage than DP1. In addition to the perils covered under DP1, it also protects against risks like vandalism, falling objects, and windstorms.
DP2 policies are usually more expensive than DP1 but less costly than DP3. They often include liability coverage and loss-of-rent protection, making them a more balanced choice for landlords seeking better protection without the highest price tag.
DP3 Policy (Special Form)
A DP3 policy is the most comprehensive and, consequently, the most expensive option. Unlike DP1 and DP2, it provides open-peril coverage, meaning it protects against all risks except those specifically excluded in the policy.
Common exclusions may include:
- Neglect
- Intentional damage
- Water damage from non-covered perils
- Mold, rust, and rot
DP3 policies typically come with liability protection and rental income reimbursement, making them the preferred choice for landlords who want maximum coverage and peace of mind.
Tips for Lowering Landlord Insurance Rates
Beyond asking for discounts, there are several proactive ways to reduce your landlord insurance costs. Some strategies can lower your premium immediately, while others help prevent future claims, keeping rates affordable over time.
Increase Your Deductible
Increasing your deductible is an effective way to lower your insurance premium, but it’s important to strike a balance between savings and affordability.
A higher deductible means you’ll pay more out-of-pocket before your coverage applies, so it’s crucial to choose an amount that won’t strain your finances in the event of a claim. This strategy works best for property owners with sufficient savings to cover unexpected expenses while still benefiting from reduced premium costs.
Maintain Your Property Regularly
Regular maintenance of your rental property is essential for both minimizing risks and keeping your insurance costs manageable. Well-maintained properties are less likely to experience damage. That means a lower likelihood of filing a claim that could drive up premiums.
Routine inspections and updates to plumbing, electrical systems, and roofing are a good way to help prevent costly issues before they escalate. Addressing minor repairs early can save money in the long run and ensure your property remains in good condition.
Review Your Policy Annually
Reviewing your insurance policy annually is a smart way to ensure you have the right coverage at the best possible rate. Over time, your property’s value and risk factors may change. The cost of building materials and comparable properties may also fluctuate, so it’s a good idea to reassess your policy to avoid overpaying or being underinsured.
Regularly checking your coverage ensures it still aligns with your needs and adequately protects your investment. Additionally, comparing quotes from different insurers can help you find competitive rates and potential savings while maintaining the necessary protection for your rental property.
How to Choose the Right Landlord Insurance Policy

With so many landlord insurance options available, it’s important to find coverage that aligns with your property’s unique risks. Here’s how to make an informed decision:
1. Assess Your Coverage Needs
Every rental property comes with its own set of risks. Consider key factors such as location, property value, and tenant type. If your property is in a flood-prone area or a bushfire zone, ensure your policy includes those protections. Understanding these risks will help you determine the right coverage limits and policy features.
2. Compare Policies and Quotes
Don’t rush into the first policy you find. Getting quotes is a pain, but spending a little bit of time may net you a lower rate with better coverage. Request quotes from multiple insurance providers and compare their coverage details, exclusions, limits, and costs. If you need guidance, I can help you navigate this process to find the right fit.
3. Research the Insurer’s Reputation
An insurance policy is only as good as the company backing it. Look for reviews and ratings from other landlords to assess the reliability and customer service of different insurers. A trustworthy provider should have a solid track record of handling claims fairly and efficiently.
4. Consider Additional Coverage Options
Standard policies may not cover everything your property needs. Think about optional coverages that could provide extra security, such as flood insurance, rent loss protection, or liability coverage. Tailoring your policy to your specific situation can save you from financial setbacks in the long run.
5. Read the Fine Print
Before committing to a policy, carefully review the terms and conditions. Pay close attention to exclusions, deductibles, and coverage limitations. Understanding these details upfront can prevent unexpected surprises when you need to file a claim.
6. Review Your Policy Regularly
Your property’s needs can change over time, whether due to market conditions, renovations, or new tenant arrangements. Make it a habit to review your policy annually to ensure it still provides adequate coverage. Adjustments may be necessary to keep your investment fully protected.
Conclusion: Protect Your Property and Have Peace of Mind
Owning rental property can be rewarding, but it comes with a range of risks and hard work. Landlord insurance offers a safety net against these risks, ensuring you don’t lose sleep over unexpected disasters, tenant-related issues, or liability claims.
To protect everything you’ve worked so hard to build, choose a landlord insurance policy that matches your needs. Those should include, property type, tenant profile, and financial goals.
